What is a package manager in Linux?
Linux uses packages to install and run the software.
A package manager is a tool that helps you find and install these packages.Package managers have a list of available packages and take care of downloading and installing them for you.
They also keep your software up-to-date by checking for updates and installing them for you.
Using a package manager is an easy way to manage the software on your Linux system.
what is a package?
A package in Linux is a complete software bundle that contains everything needed to install and run a program, including code, configuration files, documentation, and other required software components.
A package manager is a tool that helps you find and install packages easily, by automatically downloading and installing them along with their dependencies. This makes it simple and efficient to install and manage software on a Linux system.
Different kinds of package manager
There are different kinds of package managers as follows:
dpkg and apt: These package managers are used by Debian and Ubuntu to install and remove packages, and to automate common package management tasks.
RPM and YUM/DNF: These package managers are used by Red Hat, CentOS, Fedora, and other RPM-based distributions to install and remove packages, and to automate common package management tasks.
Pacman: This is a package manager used by Arch Linux that is known for its simplicity and speed.
Portage: This is a package manager used by Gentoo Linux that compiles packages from source code to create custom installations.
Flatpak: This is a newer package manager that allows for easy and consistent application deployment across different Linux distributions by containing everything needed to run the application.
Install docker in your system from your terminal using package managers.
step1: To install docker, first update the system by typing the command
sudo apt update
step2: Now, typesudo apt-get install docker.ioand type 'Y'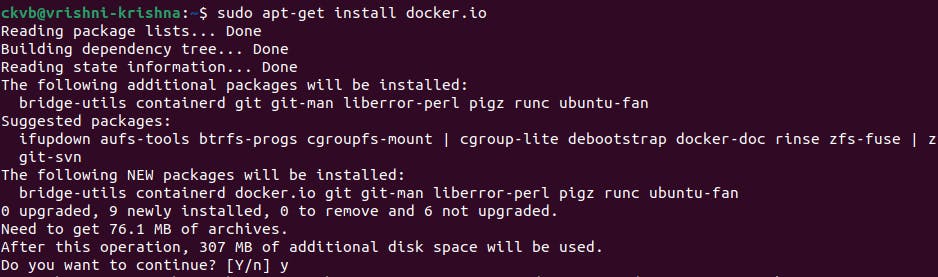
step3: Now check, whether it is installed or not by typing
docker --version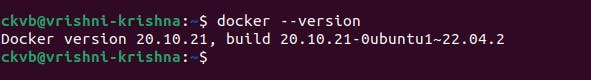
Hence, docker is installed in your system.
Install Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers.
To install Jenkins, first we need to install Java in the system.
step1: To install Java, first update the system by typing the command
sudo apt update
step2: Then, type the commandsudo apt-get install default-jdk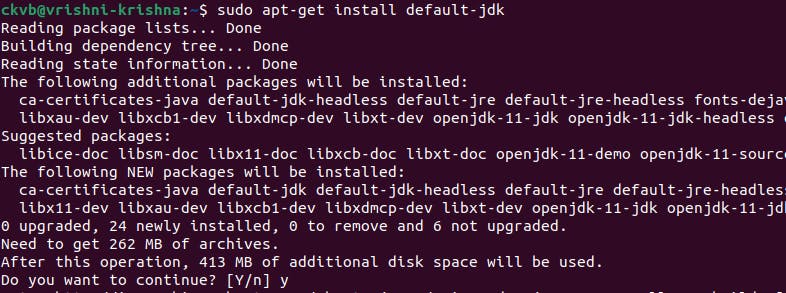
step3: Now check, whether it is installed or not by typing
java --version
Step 4: Now, you are ready to install Jenkins in your system.

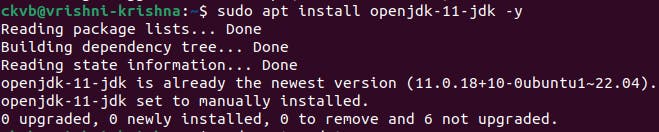
Type both the above commands, and
Just Follow 👉 Steps to install JenkinsStep 5: Once you follow the above steps & link. Just type
sudo apt install jenkinsand check whether it is installed or not
by using the commandjenkins --version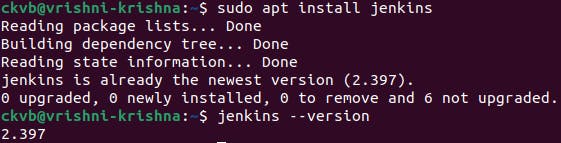
Hence, Jenkins is installed in your system.
To check the status of Docker before and after while running in your system.
Typesudo service docker status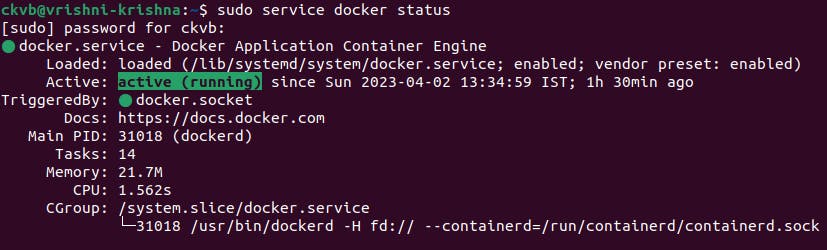
When Docker is inactive/stopped 👇
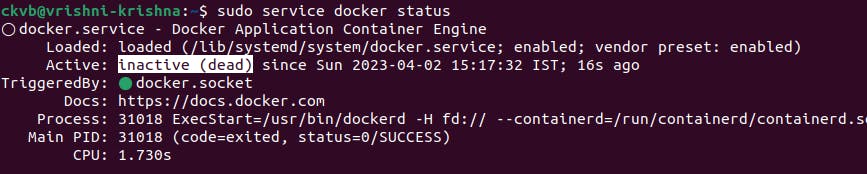
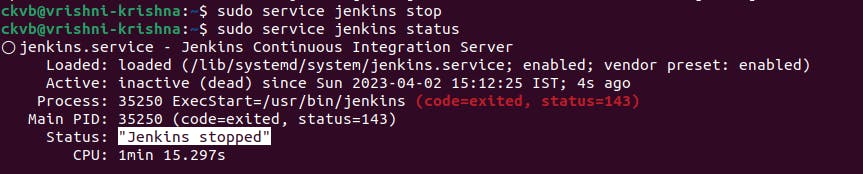
To check the status of Jenkins before and after while running in your system.
Typesudo service jenkins status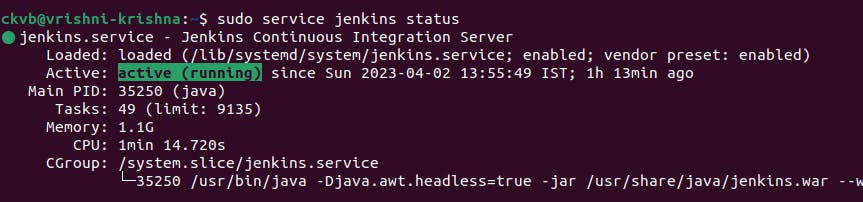
When Jenkins is inactive/stopped 👇
Difference between systemctl and service.
we can see the status of Docker and Jenkins even using systemctl command
Ex:systemctl status docker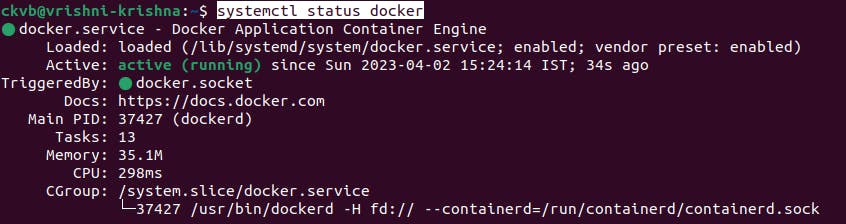
Ex:
sudo service jenkins status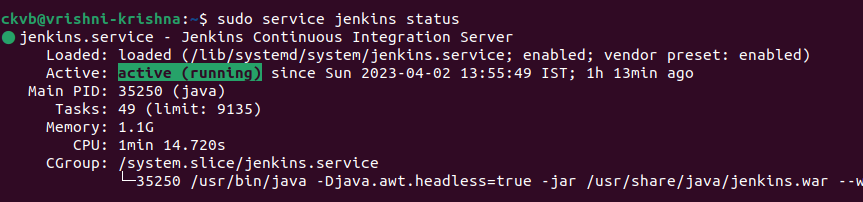
Then, what is the difference between systemctl and service when both are producing the same results 🤔
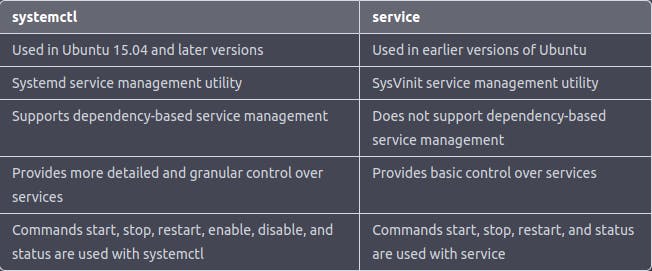
Overall, systemctl provides more advanced and powerful service management options compared to service, which is a simpler and more basic service management tool.
Thank you so much for reading.
Follow me at LinkedIn to see interesting posts like this : )
